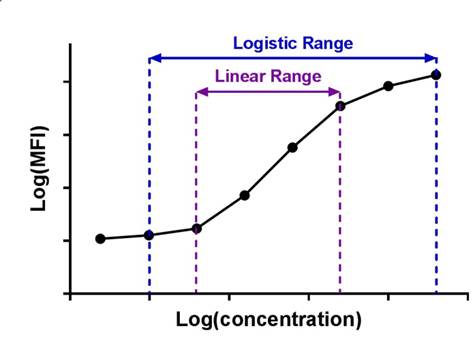
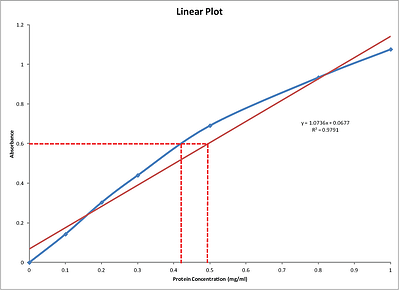
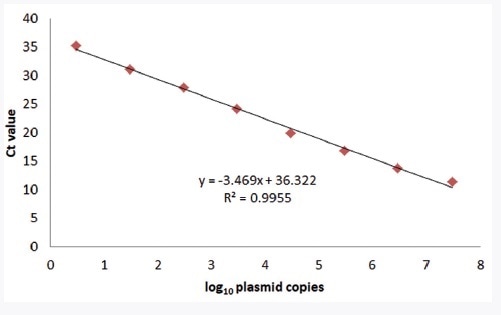
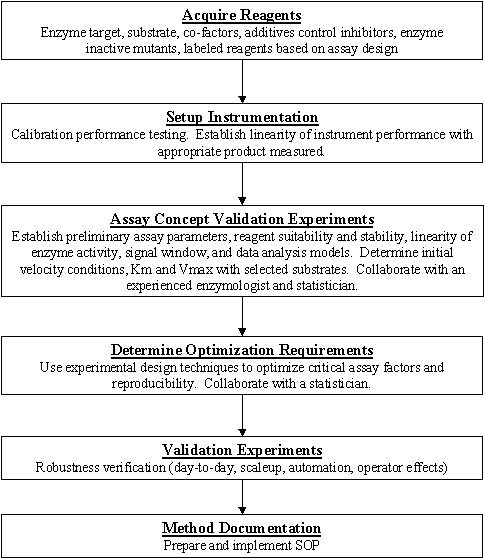
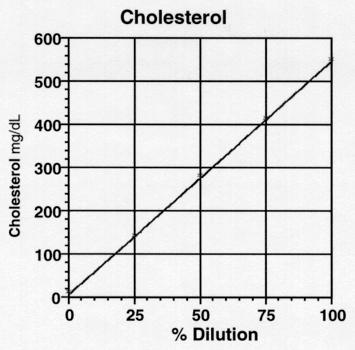
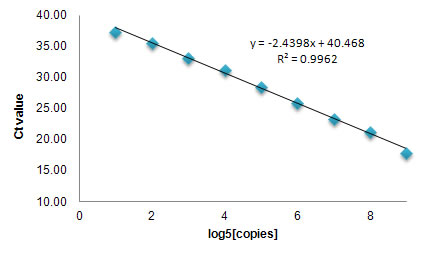
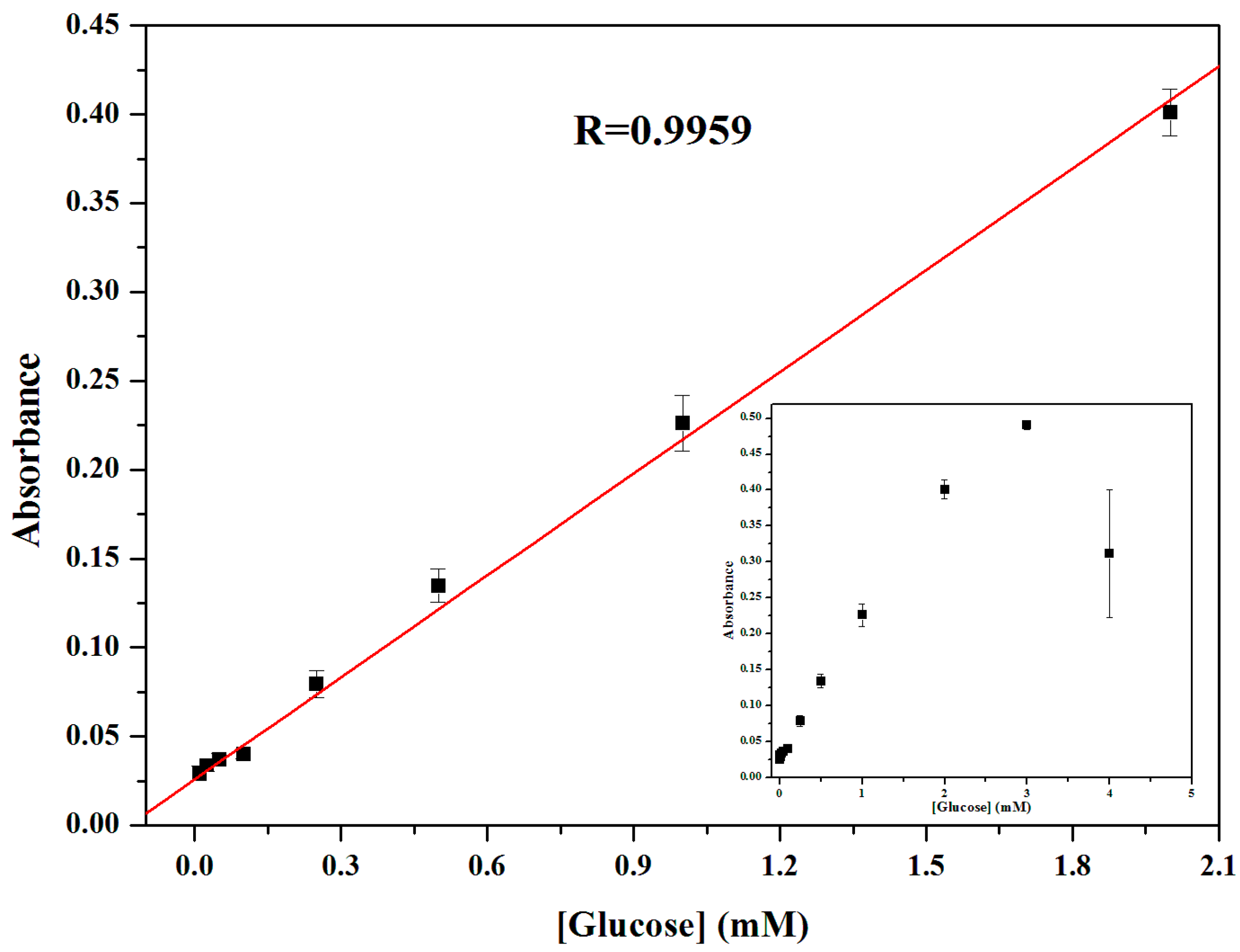
Linearity of dilution experiments are used to determine what concentrations of a given biological matrix are compatible with the assay and define the linear range of the assay for that biological sample.
Linear range of assay.
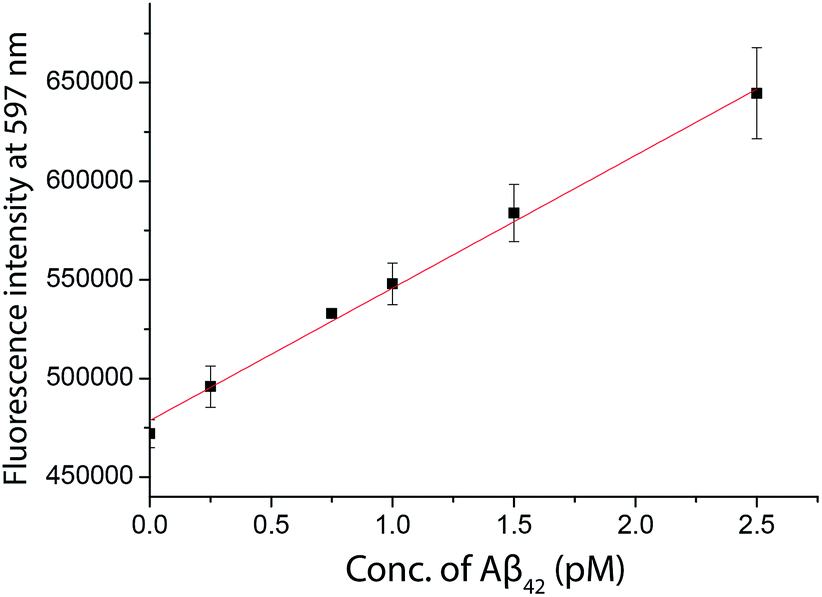
We generally try to work within the linear range of an assay that is where absorbance is directly proportional to concentration.
Within the linear range of the assay 5 25 mcg ml the more protein present the more coomassie binds.
As long as the appropriate curve fit is used an assay does not need to be linear to be accurate.
The method is based on the proportional binding of the dye coomassie to proteins.
If an amplifier were perfectly linear no distortion harmonic distortion or.
About aaron azure aaron has over 10 years lab experience with his particular interests including western blotting elisa all kinds of immunofluorescent microscopy and the exciting developments that new imaging systems.
Reportable range includes analytical measurement range amr and clinically reportable range crr.
Under acidic conditions the red form of the dye is converted into its blue form binding to the protein being assayed.
Anionic blue neutral green and cationic red.
While a linear range for the lc ms instruments is usually fairly narrow and depends on the compound several possibilities.
That is the output can be represented by the equation.
A linear range should cover 0 150 or 50 150 of the expected analyte concentration.
When operating in the linear range no clipping occurs.
A linear range can be found from the linearity assessment experiments however the criteria for a linear range can be different.
Few if any protein assays are perfectly linear over the entire useful assay range.
Output input gain.
The bradford assay a colorimetric protein assay is based on an absorbance shift of the dye coomassie brilliant blue g 250 the coomassie brilliant blue g 250 dye exists in three forms.
The approximate linear range of each analyte is generally specified by the manufacturer or in the literature but should be confirmed by each laboratory.
Reportable range should not be confused with reference range.
Ideally we would set up standards that encompass the entire useful range of an assay.
If curve fitting must be done manually a point to point fit will usually be more accurate than a linear fit to the entire range of standard points see figure.
Imaging systems such as the c600 are able to image across a much wider dynamic range and therefore linear range of detection.
Reportable range is the functional range of an assay over which the concentrations of an analyte can be measured with acceptable accuracy and precision.
If a linear relationship between analyte concentration and method response is not obtained it will be impossible to report quantitative patient results by that method.
That is we optimize the range of the assay.
The linear range is that range of input or output values for which an electronic amplifier produces an output signal that is a direct linear function of the input signal.